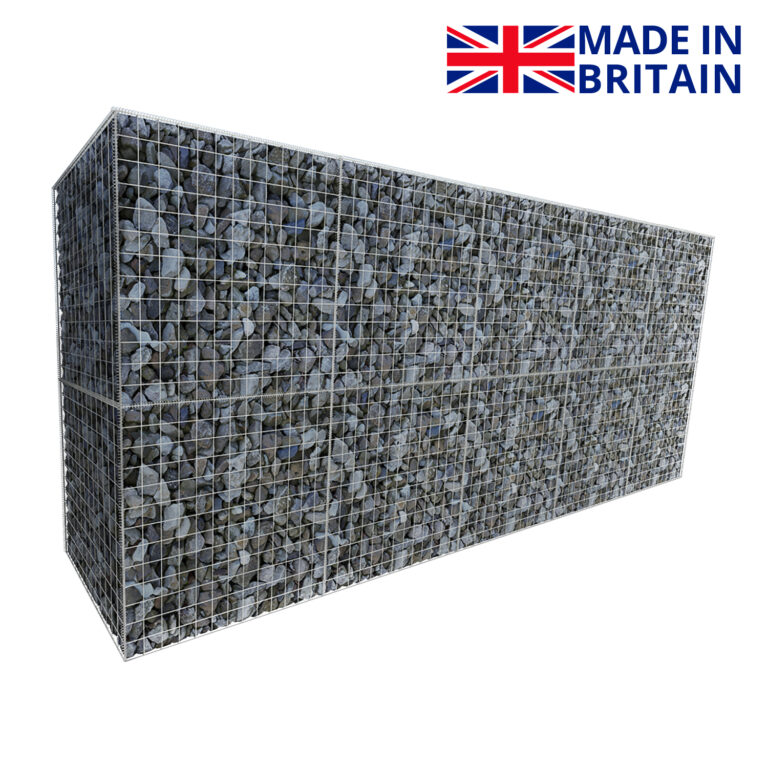
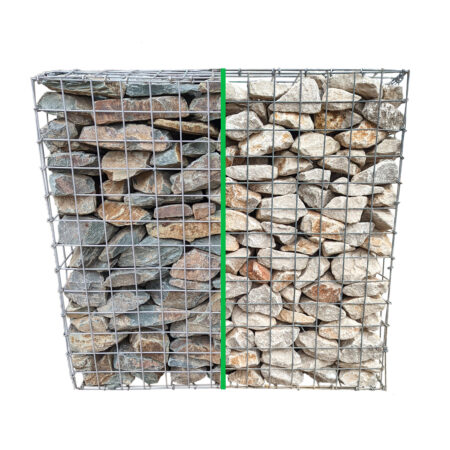
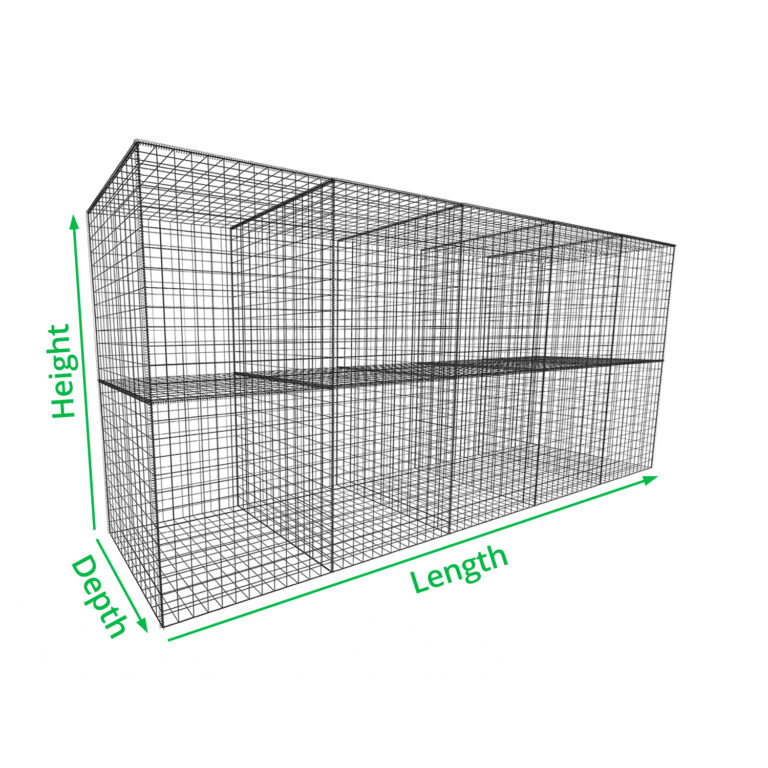
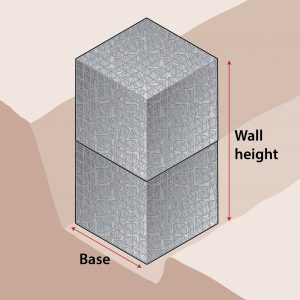
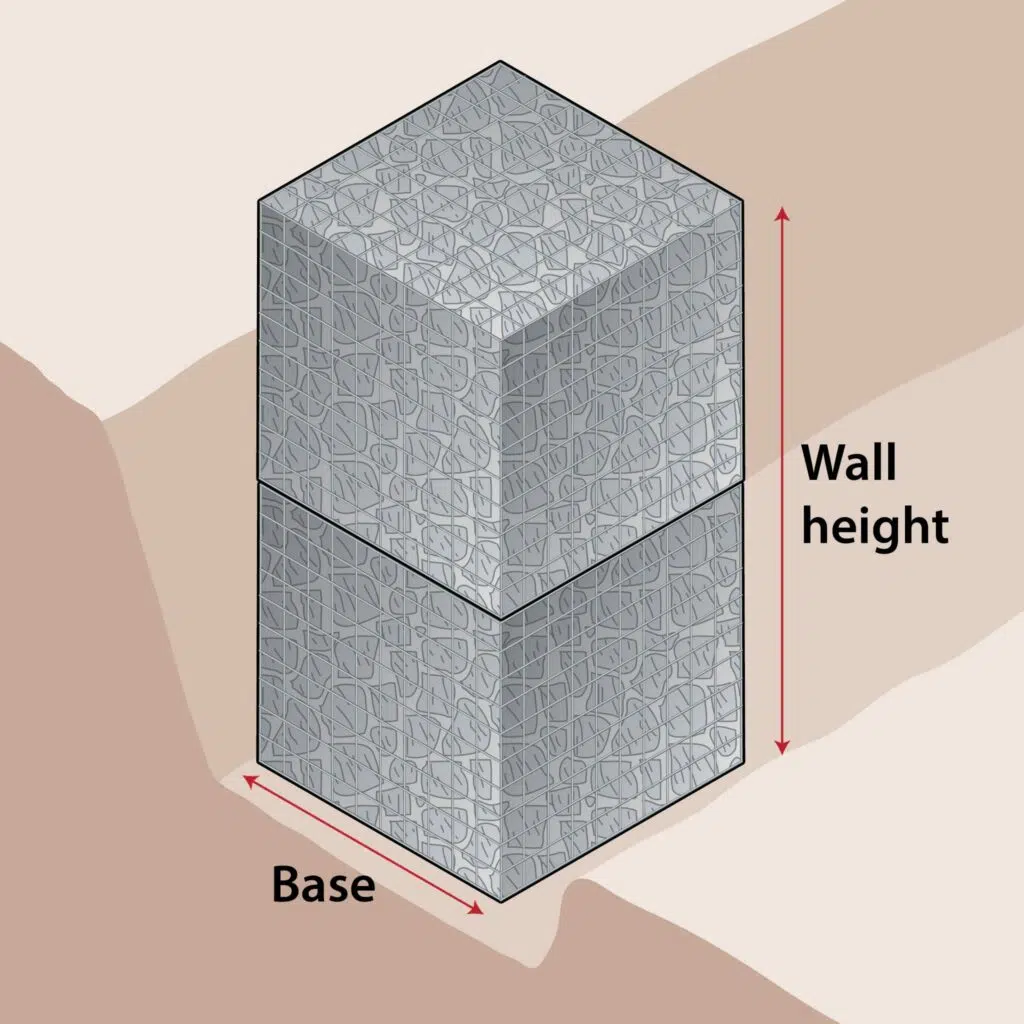
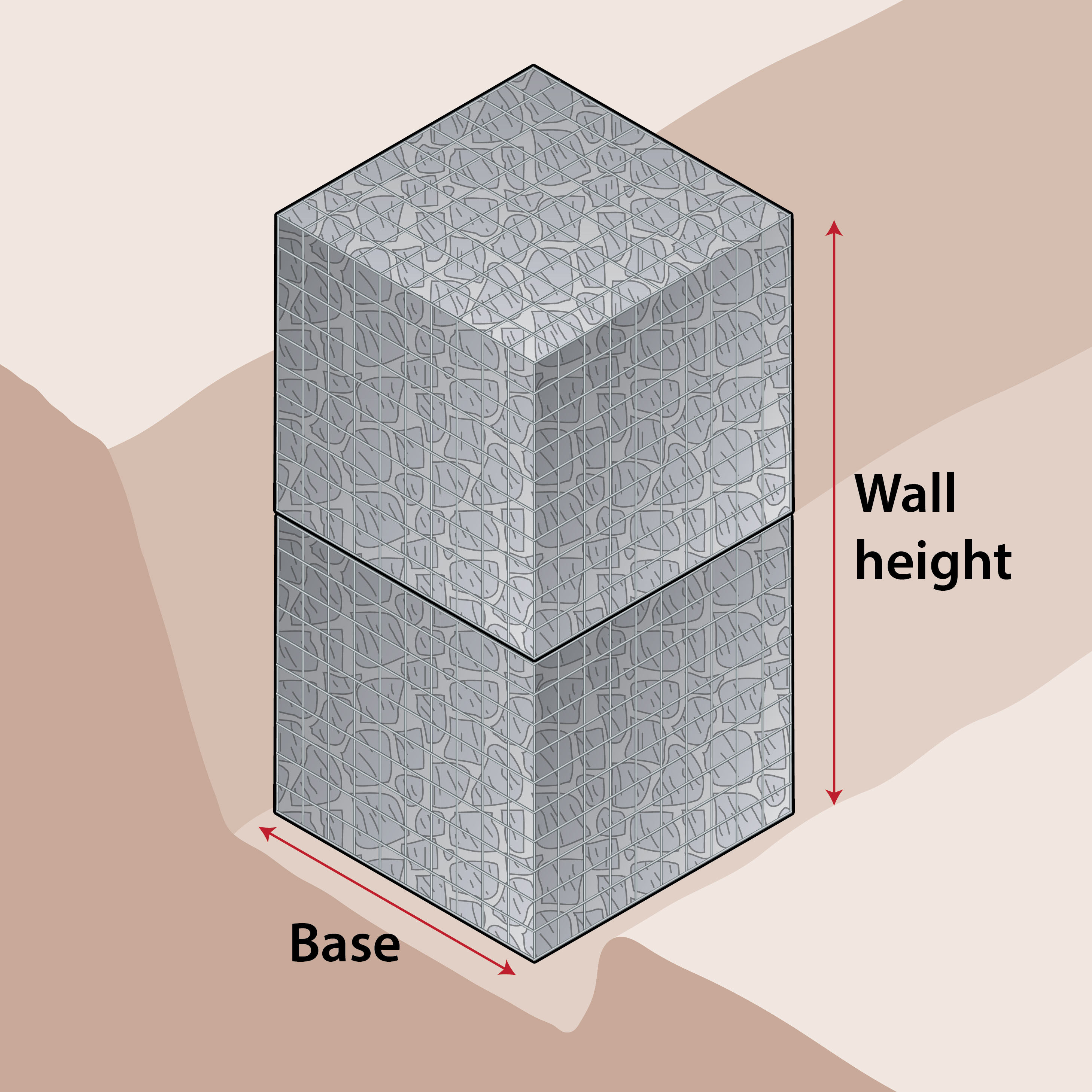
Gabion Wall Creator
Use the calculator below to quickly create a retaining gabion wall. Simply select the height and length required and the calculator will put together a list of the gabions required.
If you already know the gabion sizes you require click here
Key Info
- Manufactured to BS EN standards.
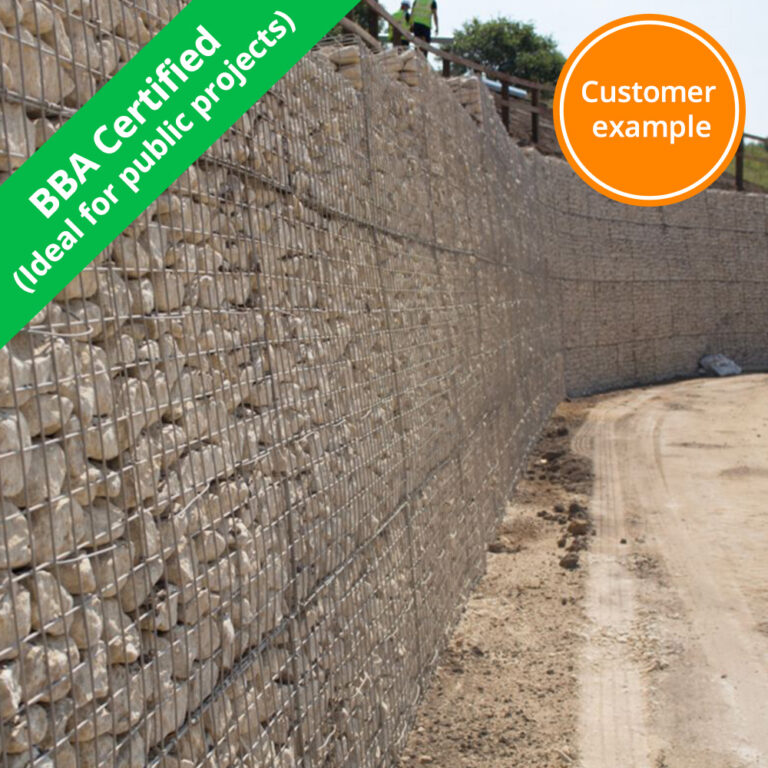
- BBA approved
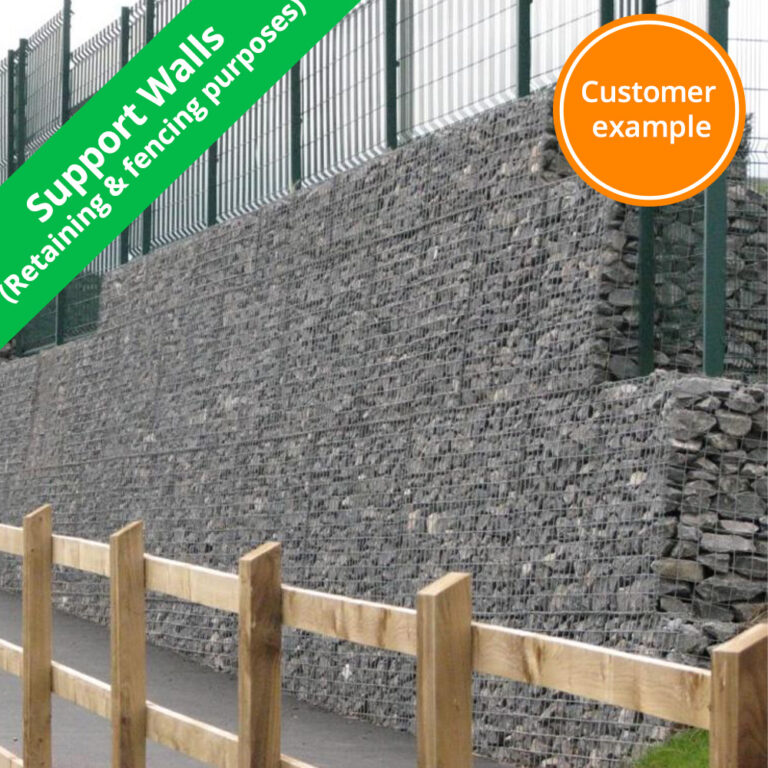
Customer Projects
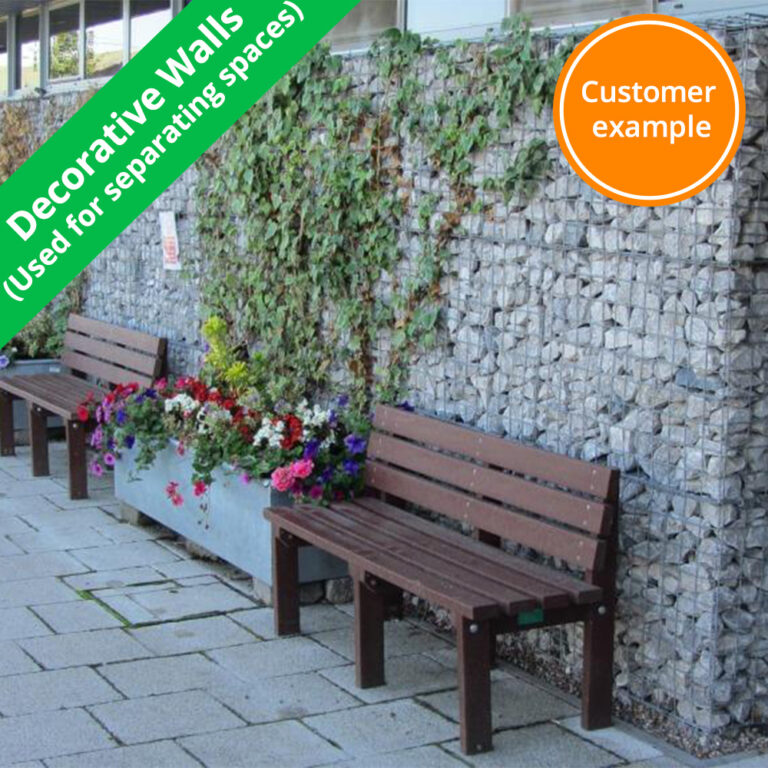
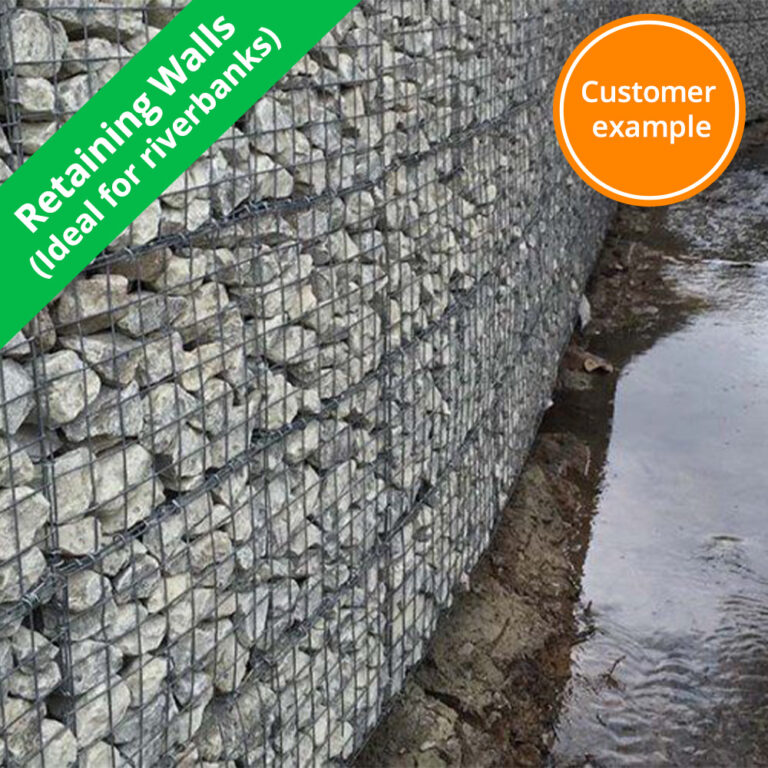
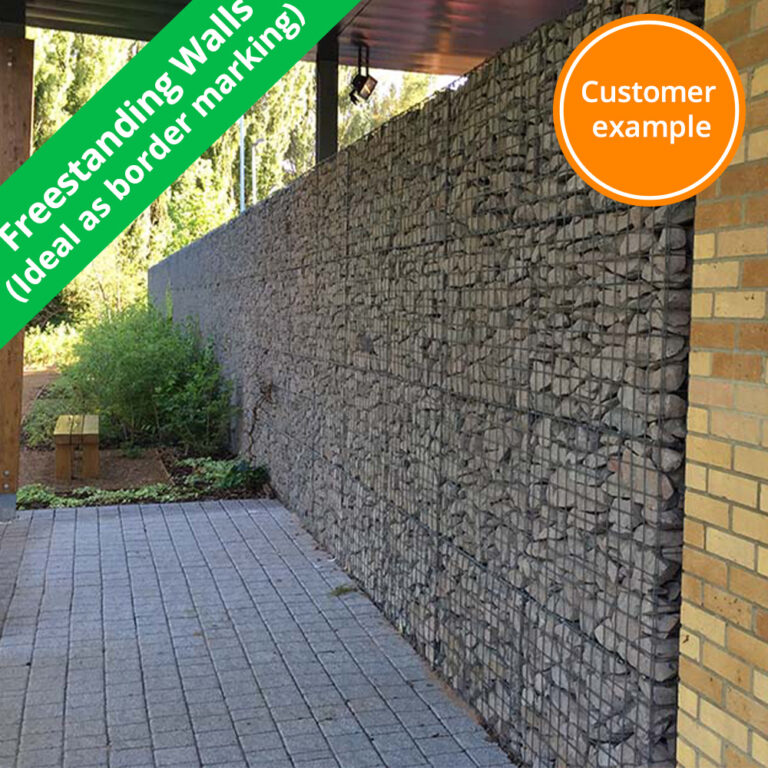
Recommended applications & uses
| Galfan Coated | PVC Coated | ||||
| 3mm Wire Diameter | 4mm Wire Diameter | 5mm Wire Diameter | 3.2mm Wire Diameter | 4.3mm Wire Diameter | |
| Freestanding wall | |||||
| Retaining walls (up to 5m) | |||||
| Retaining walls (5m and over) | |||||
| Erosion control | |||||
| Coastal protection | |||||
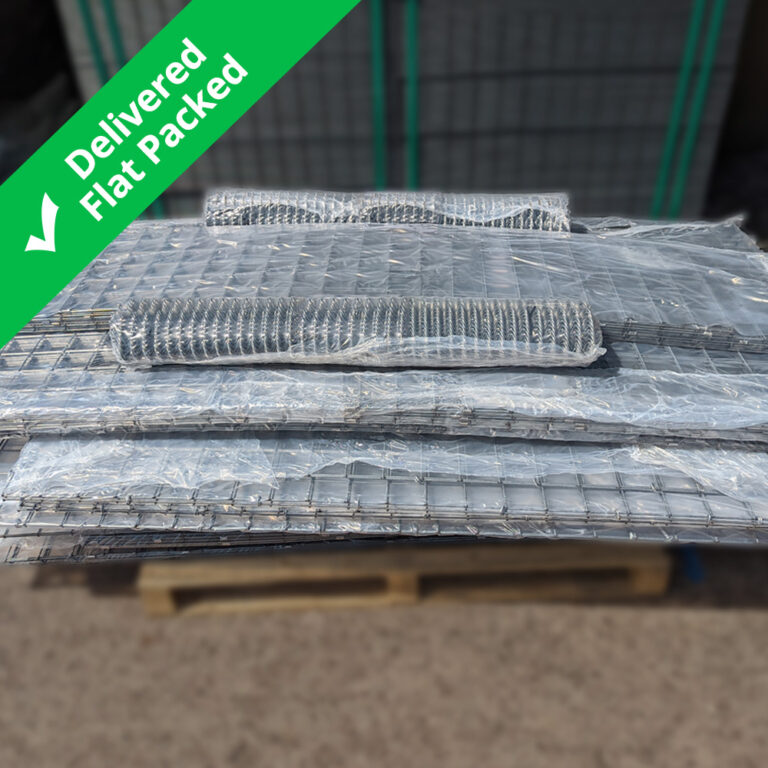
| Delivered as | Flat packed in small to large truck depending on order quantity | ||||
| Delivered with | Delivered with FREE tying wire | ||||
| Also available | Helicals – often used instead of tying wire to assemble gabions (4 pcs/basket; ordered separately) | ||||
| Also available | Corner ties to prevent bulging | ||||
| Can wires be cut | Yes – with a good wire cutter | ||||
| Made in UK | Yes | ||||
| Conforms to British manufacturing standard | BS EN 10223-8:2013 | ||||
| Certificate of conformity | Yes – download | ||||
| Construction | |||||
| Mesh Hole Size | 75mm x 75mm | 75mm x 75mm | 75mm x 75mm | 75mm x 75mm | 75mm x 75mm |
| Mesh Material | Galfan coated steel | Galfan coated steel | Galfan coated steel | Galfan coated steel with PVC coating | Galfan coated steel with PVC coating |
| Mesh Construction | Welded | Welded | Welded | Welded | Welded |
| Mesh panels joined together by | Stainless steel C Clips | ||||
| Strength and environment | |||||
| Tensile strength range | 540-770 N/mm² | 540-770 N/mm² | 540-770 N/mm² | 540-770 N/mm² | 540-770 N/mm² |
| Corrosion resistance | Yes, conforms to British standard BS EN 10244-2:2009 | ||||
| Abrasion resistance | Conforms to EN 60229:2008 | ||||
| Life Expectancy | 50 – 100 years | 50 – 100 years | 50 – 100 years | 120 years |
120 years |
| Suited to Environments | C2 – C4 | C2 – C4 | C2 – C4 | C2 – C5 | C2 – C5 |
| Rocks / Filling / Installation | |||||
| Speed of installation | 2-5 mins each | ||||
| Experience required to install | None – Download installation PDF | ||||
| Depth of structure | Minimum half of the height | ||||
| Rock size required | Minimum 80mm x 80mm | ||||
| Requires angular, interlocking rocks | |||||
| Can be filled with crushed concrete | |||||
| Can fill with rounded rocks | |||||
Assembly Fittings
| Corner Assembly Fitting | |
| How to assemble | Gabions are delivered flat packed with the sides, bottom and lid clipped together. Upon arrival, the corners of the gabions should be attached to complete assembly. |
| Using tying wire | Tying wire is supplied with all gabion orders.
PRO: it’s free |
| Using helicals | Helicals can be purchased separately. 4x helicals are required for assembly per gabion (one for each corner).
PRO: looks uniform and quick to install |
| Using CT35 clips | Gabion clips are available in bulk quantities. Advised for use by professionals
PRO: discrete / hidden |
Foundations Guide
| To Do | Explanation |
| Step 1 – Survey
|
Have a civil engineer to Identify the area that the wall should be placed |
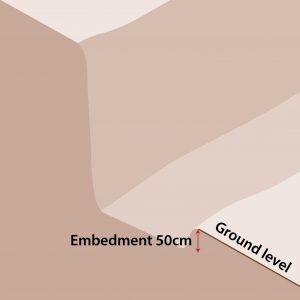
| Step 2 – Excavate
|
Regulations state that retaining walls should start at 500mm below ground but smaller walls are often placed at ground level. |
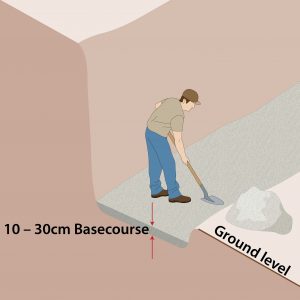
| Step 3 – Add Basecourse
|
Add a layer of Type 1 basecourse made up of crushed Granite Limestone, Basalt or Gritstone.
1m high = 100mm bascourse |
| Step 4 – Compact Basecourse
|
Use a plate compactor to compact the basecourse |
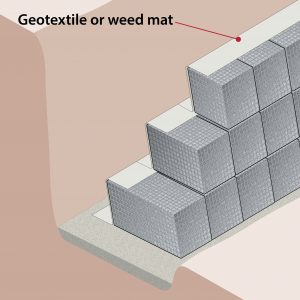
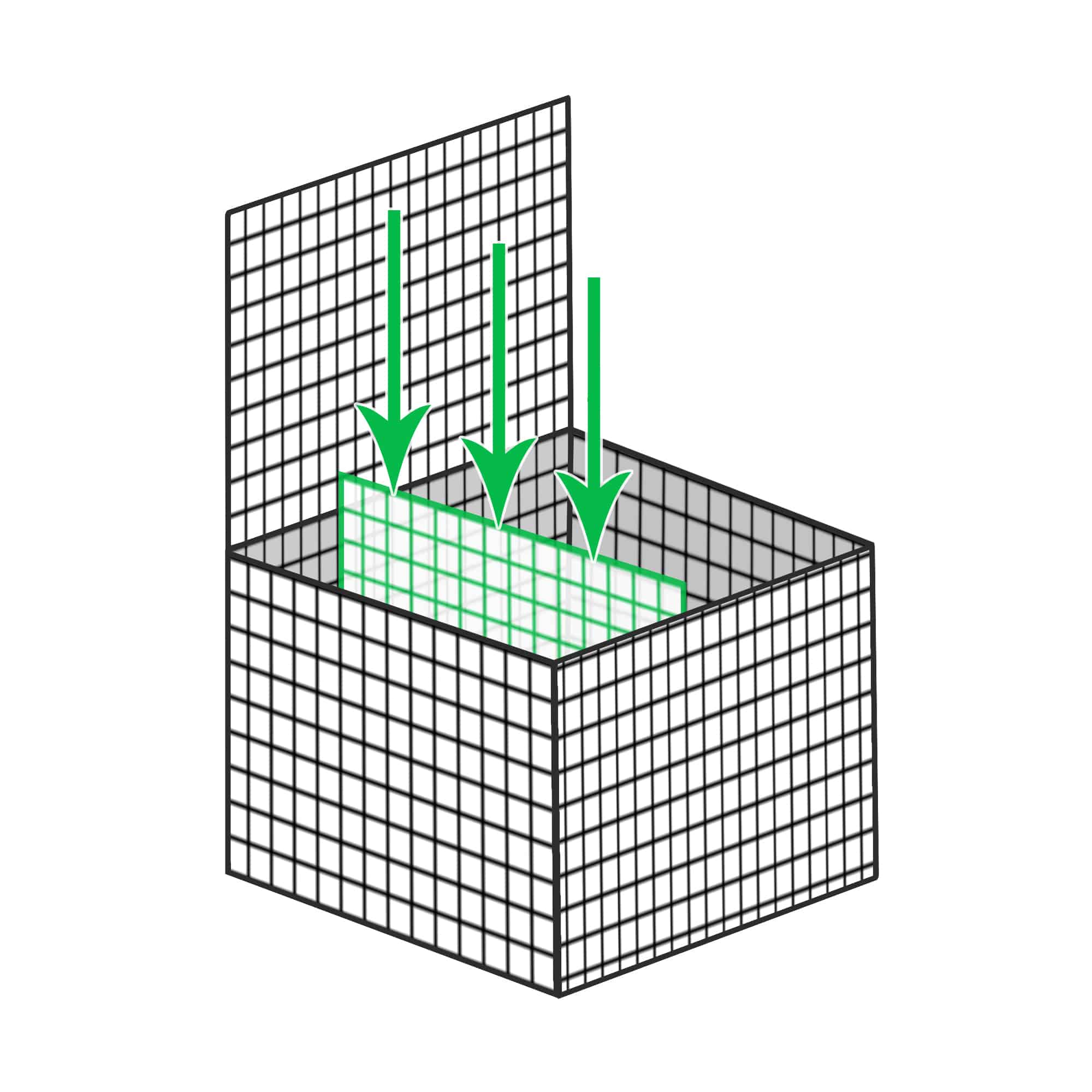
| Step 5 – Geotextile
|
Cover the back of the gabions with a geotextile or weed mat to prevent soil and earth clogging up the gabions. |
| Step 6 – Concrete Foundation (If Required) | Most gabion walls do not require a foundation.
If you have a large amount of groundwater or the soil that you are placing the gabions is weak consult a Civil Engineer They can perform a Scala Penetrometer foundation test to accurately measure the strength of the soil. |
Stability Guide
| To Do | Explanation |
| 2:1 Ratio
|
The height of the retaining wall should not be more than double the size of the base. |
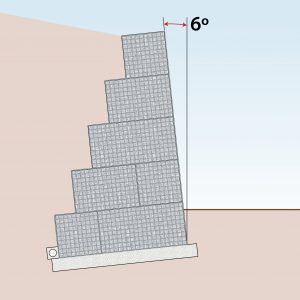
| 6 Degree Slope
|
The wall should be on a 6-degree slope.
It’s possible to have a straight wall but they need to be thicker |
| Base Width
|
The wider the base the lower the pressure on the soil. Spreading the load in this way allows for the wall to be placed on weaker soils. |
| If in doubt consult Civil Engineer |
Drainage Guide
| Diagram | Explanation |
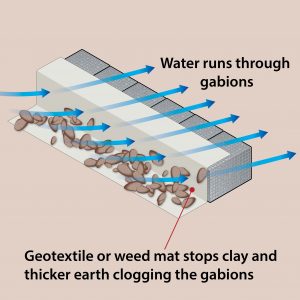 |
Gabions are porous allowing water to run through and prevent pressure build-up that can cause other types of retaining walls to collapse.
When installing the gabions ensure that a geotextile (commercial jobs) or a weed mat (residential jobs) is covering the back of the gabions. This will stop clay and thicker earth clogging up the gabions and preventing water from getting through. |
FAQs
What is a Retaining Wall?
They are a structure designed to keep earth within the desired area. Often built to prevent soil from sloping into unwanted areas such as motorways.
What is a gabion wall?
A popular and economical type of retaining wall. Made of large metal cages filled with stone, they can be stacked on top of each other to prevent earth from falling into unwanted areas.
How long does a gabion wall last?
In normal environmental conditions you can expect 50 to 100 years if the gabions meet the British Manufacturing standards for abrasion (EN 60229:2008) and corrosion (BS EN 10244-2:2009).
How expensive are gabion walls compared to other options?
Yes, they are cheaper than most other construction materials such as concrete that might be used for retaining walls. Gabions are also very easy to use, reducing the need for pay for extra manpower.
What depth should the structure have?
If it’s going to be freestanding, the depth should be at least half of the overall height in order to keep it stable. If it’s going to be reinforced with metal frames for example, you can get away with a smaller depth.
Where do I get the stone?
We supply stone suitable on this page.
You can also calculate the exact amount of stone you need on this page
In the UK there are also many quarries that can deliver stone fill to you. You can Google ‘Quarry in [INSERT LOCATION]’ and you will find someone who can help. Alternatively, please get in touch and we would be happy to send you contact details of a quarry near you.
Stones are heavy and cost a lot to transport so it is much more economical for our customers to use local stones where possible.